ClonePix technology for rapid screening and development Breast cancer cell line with high expression of GPCR 1. Cell line: CHO-M1 cell line expressing endogenous G protein-conjugated oxalin 1 choline receptor ( ATCC, M1 WT3-CRL1985 ) . Parental CHO-K1 cells were used as negative controls. 2. Antibody: rabbit anti- ChRM1-PE label, polyclonal antibody ( Bioss , Cat.#ABIN668656 ) ; rabbit anti- CHRM1 polyclonal antibody, no label; ( Bioss , Cat.#bs-1150R ) ; goat anti-rabbit IgG-PE label , polyclonal ( Life Technologies, Cat. #P2771MP ). 3. Medium: Ham's F12 medium ( Coring cellgro, Cat. #10-080-CV ); CloneMedia-CHO-S (Molecular Devices, Cat. #K8710); Fetal Bovine Serum (Hyclone, Cat.#SH30071.03 ), 1% Pen/Strep/Glutamine (Life Technologies, Cat. #10378016), 450 μg/mL Geneticin, G418 (Life Technologies, Cat. #10131035) . 4. Reaction Buffer: 10X HBSS (Life Technologies, Cat. #14065056) diluted with sterile water for injection. (Irvine Scientific, Cat. #9309) , 20 mM HEPES (Life Technologies, Cat. #15630080).  The pH was adjusted to 7.4 . 5. FLIPR® Calcium 6 Assay Kits (Molecular Devices, Cat. #R8190) . 6. Microplates : 6-well non-TC treated, clear-bottom plates (Greiner Bio-One, Cat. #657185); 384-well black-wall, sterile, TC-treated, clear-bottom plates (Corning, Cat. #3072) . 7. M1 AChR agonist: Carbamoylcholine chloride or Carbachol (Sigma, Cat. #C4382) . Isoprene Gasket For Caps,Gasket for Medical Bag,Isoprene Rubber Gasket SUZHOU CRH PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.crh-health.com
ClonePix Technology Rapidly Screens and Develops Mammal Cell Lines with Highly Expressed GPCR - Molecular Devices ClonePix 2
ClonePix TM 2 System provides a new and rapid method for assessing GPCR target protein expression levels in mammalian cell lines
1. Rapid assessment of endogenous expression levels of GPCR target proteins using a lactation expression system
2. Increase the likelihood of finding the optimal cell reactor
3. Reduce the time of cell line / antibody development - avoid limited dilution
background
The endogenous expression of GPCRs in mammalian cells is usually very low, typically no more than 3,000 copies per cell. These endogenous expression levels are sufficient to maintain normal receptor function, but there are challenges in the application of GPCR drug discovery. Most screening assays require higher concentrations of functional GPCRs to be present on the cell surface. For example, structural studies, small molecule drug design, and functional antibody production of native GPCRs require that GPCR expression levels be several orders of magnitude of endogenous expression levels. The success of attempting to establish an expression system in "lower" organisms is very limited due to the inefficient folding of bacteria; the low yield of yeast and the incorrect post-translational modification of baculovirus. These challenges have spurred market demand for high expression of GPCR protein mammalian cell lines in drug discovery applications.
With regard to the development of cell lines, it is very challenging to find and screen highly expressed GPCR clones from transfected cell banks. ClonePix technology has been demonstrated to rapidly screen large numbers of heterologous cells in one step (10,000 clones per week). Since extremely large cell banks can be screened, the possibility of finding an optimal cell producer is greatly increased. Using white light and fluorescence in situ imaging, the ClonePix 2 system is sufficiently sensitive to detect endogenous proteins with limited expression on the cell surface.
method
The transfected cell line CHO-M1 expressing the endogenous G protein- conjugated oxalin 1 choline receptor (GPCR-M1) was selected to demonstrate the feasibility of the ClonePix2 system for detecting cell surface expressed proteins. CHO-M1 expression clones were screened with PE-labeled anti-M1 antibodies, and ClonePix2 was selected and selected based on fluorescence intensity. The wild type CHO-K1 cell line served as a negative control. The CloneSelect Imager system, which objectively evaluates cell growth and label-free techniques, was used to monitor the proliferation of cells selected by the ClonePix2 system. The FLIPR Tetra High Throughput Cell Screening System and the FLIPR Calcium 6 Kit were used to verify the function of the ClonePix2 system to isolate cell clones. The FLIPR Tetra system uses calcium-sensitive fluorescent reporter dyes for high-throughput functional cell assays and is the tool of choice for assessing intracellular calcium responses in GPCR activation in drug discovery studies.
material
Instrument overview
ClonePix 2 System
1. An automated system for screening and picking clones of mammalian cells
2. White light and fluorescence imaging
3. Transmitted light supports low-contrast clones such as single-layer adherent cell imaging
4. Software Control 5 Switching of Excitation/Emission Filters
5. User-defined criteria for clone sorting
6. Target clone identification and picking to 96-well target board
7. Support multiple applications of suspended and adherent cells
1. Screening and picking hybridoma cells that secrete antigen-specific antibodies
2. Cell line development
CloneSelect Imager
1. Labelless white light cell imaging technology
2. Objectively and quantitatively evaluate cell growth
3. Simple, easy to use software interface
4. Accurately obtain the growth rate of cells per well of a 96-well plate
5. Support multiple applications:
1. Monitor cell growth
2. Monoclonal verification
FLIPR Tetra system
1. Standard EMCCD fluorescence detection or optional ICCD fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection
2. User configurable 96-, 384-, and 1536-well plates
3. User replaceable suspension cell option
4. Unique, configurable excitation optics expands the application of fluorescent species
5. Intuitive, easy to use software interface
Semi-solid medium cultured cells
CHO-M1 and CHO-K1 cell lines: CHO-M1 and parental CHO-K1 cell lines were cultured in CloneMedia CHO (K8710) medium at 1000 cells per well and cultured at 37 °C for 8-10 days until discrete clones were formed. The newly passaged cells and the previous generations of cells were separately cultured in the medium, and different expression levels of M1 GPCR were observed.
Direct labeling method: PE-labeled CHRM1 antibody was added directly to the semi-solid medium with the cells. Control wells included cells but no antibodies.
ClonePix2 system imaging and picking cell clones expressing GPCR (M1)
ClonePix2 images and picks positive (CHO-M1) and negative (CHO-K1) cells. Bright field imaging identifies the location and morphology of each clone, and fluorescence imaging identifies highly expressed M1. For PE-labeled antibodies, the Cy5 channel was exposed for 6,000 ms.
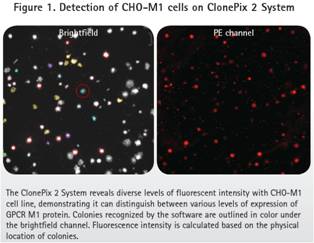
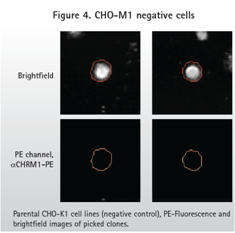
Whether it is a direct labeling method or a diabody method, CHO-M1 positive cells produce a wide range of fluorescent signals according to the ClonePix2 record. Figure 1 shows the different degrees of expression of M1 GPCR. As expected, the parental CHO-K1 cells did not produce a fluorescent signal.
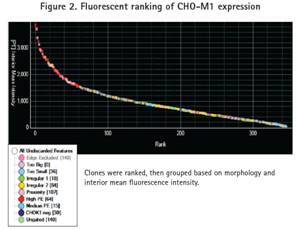
Cells are grouped based on morphology and fluorescence intensity. The morphology of the picked clones is based on size, shape, and proximity between clones. Morphologically ideal clones were ranked according to internal fluorescence intensity and gated into four fluorescence groups: high, medium, CHO-K1 negative and ungated (Figure 2). The CHO-K1 negative group was defined as the background fluorescence signal. All clones were identified corresponding to the negative control wells. An Ungated clone is a clone that has a low fluorescence signal but is higher than the background fluorescent signal.
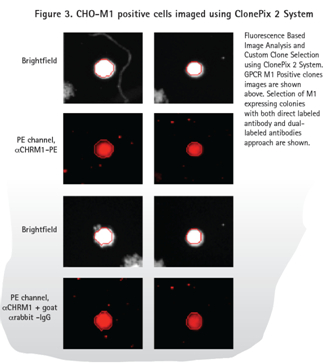
The method of directly labeling the antibody and the diabody (Fig. 3 ) shows the fluorescent signal of the positive sample (expressing M1 ) and the parental cell line without the fluorescent signal (Fig. 4 ). As expected, the diabody method produced a higher background signal in the PE channel due to the binding of the primary antibody and the secondary antibody . However, ClonePix2 detects cells in the bright field and then looks at the fluorescent signals in the cell clones. Objects identified in the PE channel but not recognized in the bright field are not considered to be clones. Therefore, the ClonePix2 system has the advantage of having the ability to distinguish true clones from background signals.
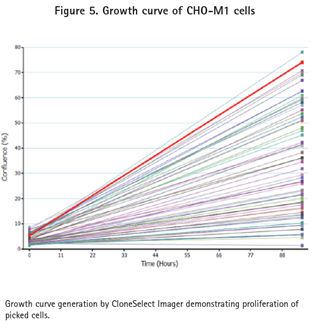
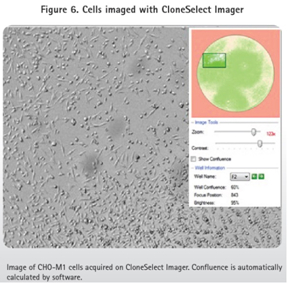
The clone CHO-M1 picked by the ClonePix2 system was stored in 96-well Greiner plates containing 200 μL of Ham's F12 media + 10% FBS + G418, while the CHO-K1 clone was stored in the same microplate but not G418. These 96-well plates were imaged in the CloneSelect Imager system to confirm cell transfer and growth (Figure 5). After one week of cell culture, CloneSelect Imager analysis was used to ensure that the cells had proliferated (Figures 5 and 6). The cells were then transferred to a 384-well plate and functionally confirmed using the FLIPR Tetra system and calcium 6 reagent.
FLIPR Tetra verification system M1 GPCR expression cells picked ClonePix2
Cell preparation
The cells picked from the ClonePix2 system were seeded into 384 wells, 25 μL of medium per well, 5,000 cells, 37 ° C, 95% humidity and 5% CO 2 overnight. These cells were sorted into four groups: high, medium, low, and no M1 expression.
Add calcium sensitive fluorescent dye
The cell culture plates were removed from the incubator and equilibrated at room temperature. 25 μL of FLIPR Calcium 6 dye was added directly to the cell plate containing the medium. 2.5 Mm of probenecid was added to these wells to prevent organic ion transport and incubated for 2 hours at 37 °C. Maintain at room temperature until the fluorescence reading.
FLIPR Tetra Fluorescence Imaging Plate Reader
After incubation and room temperature equilibration, place a plate into the FLIPR system. The FLIPR system ICCD camera captures the fluorescent calcium signal. The imaging parameters are as follows:
Exposure (sec) 0.53
Excitation LED (nm) 470-495
Emission filter (nm) 515-575
LED intensity (%) 80%
FLIPR Calcium 6 Kit
Fluorescence readings per second, read 10 points before adding Carbachol, and 60 points after adding 40nm Carbachol. The initial concentration of Carbachol is 5 times the final concentration. Carbachol has a volume of 12.5 μL and a dispensing speed of 20 μL/sec.
FLIPR Calcium 6 kit validates selected CHO-M1 and CHO-K1 cell clones
Upon activation of the ligand GPCR, changes in the conformation of the receptor trigger activation of the intracellular G protein. The activated G protein has the potential to induce intracellular different messengers including calcium messengers.
The different groups of cells picked up by the ClonePix2 system were evaluated for functional activity using the FLIPR Tetra system. In a 40 nM Carbachol condition, a calcium sensitive fluorescent dye (FLIPR Calcium 6 Assays kit, Molecular Devices) was used to evaluate the feasibility of changes in calcium ions in the cytosol with changes in activated G protein-coupled IP3 sensitive pathways. Historical data indicates that 40nM Carbachol is the concentration of EC80.
Isoprene Gasket For Caps