ã€references】 (B) combined with chemotherapy for the expected effect of the population use of chemotherapy (intravenous administration) patients (oral chemotherapy and high-efficiency CIK treatment alone) improve quality of life, eliminate chemotherapy side effects, synergy with chemotherapy, kill Tumor cells maintain tumor stability. • Three-week chemotherapy regimen (3) Combination with targeted therapy The expected population The patients who are using the targeted therapy are synergistically produced by the action of ADCC and antibody-targeted therapy, and the killing of tumors improves the side effects caused by targeted drugs to maintain tumor stability. • Depending on the treatment plan of the targeted drug 4. Efficient CIK blood specimen collection and care (1) Assessment of patients before blood collection, including condition, state of consciousness, vital signs, ongoing treatment, venous filling, patient understanding and cooperation ability; 1. Application in leukemia Zhao Chunhua and other studies have shown that co-culture with DC can achieve higher proliferation rate and stronger anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo. DC-CIK cells can be used as a clinically effective anti-leukemia immunity. Treatment strategy. Clinical studies such as Tong Chunrong show that DC-CIK cell therapy has the effect of clearing small residual leukemia cells to prevent recurrence, and intravenous infusion is safe. 2. Application in tumors DC-CIK cells can be obtained by co-culturing CIK cells with homologous DC cells. It not only promotes the maturation of DC cells, but also promotes the proliferation of ClK and enhances its anti-tumor activity. DC cells are the initiators of the body's immune response, capable of inducing long-lasting and potent specific anti-tumor immune responses; CIK cells can eliminate tiny residual lesions in tumor patients through non-specific immune killing, so DCs carrying tumor antigens and organic CIK Binding (ie, DC-CIK cells) produces both specific and non-specific dual anti-tumor effects. 1. ACTL technology background 2. ACTL technical treatment mechanism Fire Extinguisher,Automatic Dcp Fire Extinguisher,Co2 Type Fire Extinguisher,Water Mist Extinguisher NINGBO TOMAN IMP. & EXP. CO., LTD , https://www.tdotmfiresolution.com

ã€background knowledge】
CIK is an abbreviation for "Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells", which is referred to as "cytokine-induced killer cells" in Chinese.
CIK is a group of heterogeneous cells in which mononuclear cells are cultured under the action of CD3 mAb and various cytokines (including IFN-γ, IL-2, etc.), and CD3+CD56+ cells are the main effector cells. The powerful anti-tumor activity of T lymphocytes has the non-MHC (major histocompatibility antigen) limiting tumor killing ability of NK cells (natural killer cells). 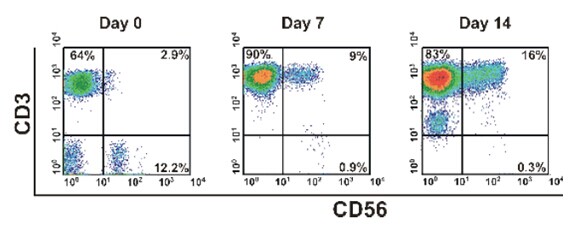
Advantages of CIK cells: high tumoricidal activity, broad spectrum of tumoricidal activity, low toxicity to normal tissues, and high amplification in vitro. It is a adoptive immunotherapy cell widely used in clinical practice.
[Culture principle]
Cytokines and antibodies for CIK culture:
1. CD3-excited monoclonal antibody:
The first signal of T cell activation comes from the receptor on the surface of T cells, that is, the specific binding of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) to the antigen presented by APC, that is, the specificity of T cells to antigen. Identification. TCR is a heterodimer composed of two different peptide chains which, on the surface of T cells, binds to CD3 molecules by non-covalent bonds to form a TCR/CD3 complex. The recognition of specific antigen by TCR causes aggregation of the cytoplasmic tail of the co-receptor CD4 or CD8 molecules on the surface of CD3 and T cells, thereby activating tyrosine kinases (Lck, Fyn and ZAP-70, etc.) linked to the cytoplasmic tail. Phosphorylation of tyrosine (Y) in the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of the cytoplasmic region of CD3 molecule. Phosphorylated tyrosine (pY) further phosphorylates downstream tyrosine-containing proteins, causing a cascade of kinase activation (phosphatidylinositol pathway or MAP kinase pathway, etc.), ultimately by activating transcription factors In the nucleus, binding to target genes (such as IL-2 and IFN-γ) that regulate T cell proliferation and activation, causing gene expression and transcription, and T cells are thus transferred from a quiescent state to a proliferating and activated state.
It can be seen from the above that CD3 molecules play an extremely critical role in the transduction of T cell activation signals. CD3-excited monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the CD3 molecule on the surface of T cells, which can cause phosphorylation of tyrosine in the ITAM motif of the cytoplasmic region of CD3 molecule, which in turn leads to activation of downstream signals of T cell proliferation and activation, thereby enabling T Cell proliferation and activation. That is to say, CD3-excited monoclonal antibody can mimic the recognition and activation process of antigen and TCR/CD3 complex, which leads to the proliferation and activation of T cells, and is therefore an indispensable stimulating factor in CIK cell culture.
In addition, CD3-excited monoclonal antibodies must pay attention to the clone number when selecting. Studies have shown that only CD3-excited mAbs with the clone number OKT-3 can stimulate the proliferation of T cells in all humans, while CD3-excited monoclonal antibodies of other clones can only stimulate some human T cells. Therefore, in the case of CIK culture, it is best to use OKT-3 clones to ensure that each patient's T cells can be activated.
2. IL-2 (Interleukin-2)
IL-2 was originally discovered as T cell growth factor (TCGF) and is the most important cytokine that causes T cell proliferation. IL-2 is both an autocrine cytokine and a paracrine cytokine that promotes T cell activation and enters a cell division state by specific binding to the IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) on the surface of T cells.
In addition, IL-2 can also stimulate the growth of NK cells and enhance their killing ability. Therefore, IL-2 must be added to CIK cell culture to promote the proliferation and activation of T cells.
3. IFN-γ (interferon-γ)
IFN-γ has the effect of up-regulating the expression of IL-2R on the surface of peripheral blood lymphocytes, thus enhancing the sensitivity and intensity of T cells to IL-2 proliferative response. The addition of IFN-γ during the induction of CIK cell formation reduces the amount of IL-2. The study found that the order of IFN-γ addition is closely related to the cytotoxic activity of CIK. The cytotoxic activity of CIK was significantly increased by adding IFN-γ first, and then adding IL-2 after 24 hours of culture.
4. IL-1α (interleukin-1α)
IL-1α also mediates up-regulation of IL-2R on the surface of peripheral blood lymphocytes. When IL-1α is combined with IFN-γ and the elicited CD3 monoclonal antibody, the cytotoxic effect of CIK can be significantly enhanced.
[Cell preparation]
1. Collection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells
1.1 using a blood cell separator to collect 50-100 mL of the patient's own peripheral blood mononuclear cells;
1.2 Lymphocyte separation solution further purification of mononuclear cells (PBMC) by density gradient centrifugation;
1.3 Serum-free medium was washed twice to obtain PBMC with a purity of 90% or more.
2. CIK cell culture and identification
2.1 PBMC was suspended in serum-free medium at a concentration of 1-2 x 106/ml, and added to a recombinant human IFN-γ at 1,000 U/ml, and cultured in a 37 ° C, 5% CO 2 incubator;
2.2 After 24 h, 50 ng/ml of CD3 monoclonal antibody and 300 U/ml of recombinant human IL-2 were added to stimulate the growth and proliferation of CIK cells;
Note: 100 U/ml recombinant human IL-1α can also be added at this time.
2.3 Change the liquid or expand the bottle once every 3 days, and add the recombinant human IL-2 300 U/ml;
2.4 On day 14 of culture, CIK cells were harvested.
2.5 CIK cell quality control:
2.5.1 Trypan blue staining test: live cells should be above 80%;
2.5.2 Flow cytometry to detect the expression of CD3, CD8, CD56 and other molecules on the cell surface: the proportion of CD3+CD56+ cells should be above 20%.
2.5.3 Cell killing experiment: Using CIK cells as effector cells, tumor cells (which may be primary tumor cells or tumor cell lines) as target cells, and effector cells and target cells are added in a ratio of 10:1 (number ratio). In the 96-well U-shaped plate, each well contained 1 x 104 target cells, and the final volume was 200 μl, and three replicate wells were set. After culturing for 4 hours, the culture supernatant was taken, and the killing rate of the effector cells against the target cells was detected by a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) kit.
2.5.4 Before harvesting the cells, take a small amount of culture for bacterial and fungal culture, and test for mycoplasma, chlamydia, and endotoxin (standard: negative for pathogen detection, endotoxin <5 Eu).
[step diagram] 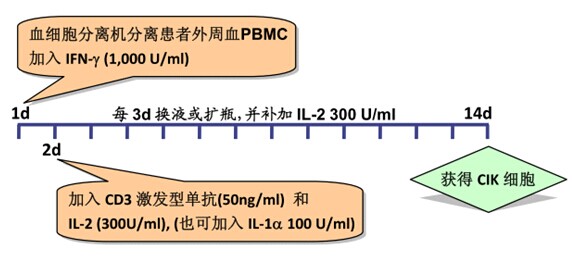
Manufacturer Product Name Product No. Product Specifications Use Concentration
eBioscience Anti-Human CD3 Functional Grade Purified 16-0037-85 500μg
PeproTech- biogems Anti-Human CD3 SAFIRE Purified 05121-25 100μg/500μg
PeproTech recombinant human IFN-γ (Animal Free) AF-300-02 100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-1α (Animal Free) AF-200-01A 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 0.1ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-2 (Animal Free) AF-200-02 50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 30ng/ml
[Recommended reagent]
Manufacturer Product Name Product No. Product Specifications
PeproTech Recombinant Flt-3 Ligand (Animal Free) AF-300-19 10μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human IL-7 (Animal Free) AF-200-07 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human IL-15 (Animal Free) AF-200-15 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human SCF (Animal Free) AF-300-07 10μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
Note: Animal Free means no animal content. The animal-free recombinant cytokine does not have any animal-derived substances in the production process, especially the incorporation of bovine protein, so that the recombinant human protein finally obtained does not contain any animal components. This can avoid contamination of animal pathogens (such as mad cow disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, etc.) and xenogeneic rejection and allergic reactions caused by foreign proteins. Therefore, it is preferable to use animal-free recombinant cytokines in cell culture in vitro.
ã€references】
[1] Li R, Wang C, et al. Autologous cytokine-induced killer cell immunotherapy in lung cancer: a phase II clinical study. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012; 61:2125–2133 
ã€background knowledge】
DC is the abbreviation of "Dendritic Cells", which is called "dendritic cells" in Chinese. It is named for its many dendritic or pseudo-protrusions. The DC was discovered in 1973 by the 2011 Nobel Prize winner and Canadian scientist Ralph M. Steinman. It is the most powerful antigen-presenting cell (APC) found today. It has been confirmed that DC is the only APC that can significantly stimulate the proliferation of naïve T cells. Mature DCs can present tumor antigens through pathways such as type II histocompatibility antigen (MHC-II), effectively resisting tumor cells. The immune escape mechanism, while other APCs (such as monocyte macrophages, B cells, etc.) can only stimulate activated or memory T cells. DC is the initiator of the body's adaptive T cell immune response and plays an extremely important role in tumor immunity.
CIK is a group of heterogeneous cells in which mononuclear cells are cultured under the action of CD3 mAb and various cytokines (including IFN-γ, IL-2, etc.), and CD3+CD56+ cells are the main effector cells. The powerful anti-tumor activity of T lymphocytes has the non-MHC (major histocompatibility antigen) limiting tumor killing ability of NK cells (natural killer cells).
DC-CIK (or DC+CIK) [1] refers to CIK cells co-cultured with DC cells, and it can be said that the final effector cells are CIK cells activated by DC in vitro. A number of studies have shown that DC and CIK have synergistic effects. After co-incubation, the expression of co-stimulatory molecules on DC surface and antigen-presenting ability are significantly improved, while the proliferative capacity of CIK and cytotoxic activity in vitro and in vivo are also enhanced, so DC- CIK is more effective than CIK alone. Co-culture of tumor antigen-loaded DCs with CIK can stimulate the production of tumor antigen-specific T cells. Such DC-CIK treatment has both specific and non-specific dual tumor killing effects, and DC stimulation without tumor antigen loading. Activated CIK is more active and is often used in clinical and scientific research.
CIK cells and DC cells are two important components of cellular immunotherapy, and the combination of the two ensures a highly effective immune response.
[Culture principle]
1. Cytokines for DC culture:
1.1 GM-CSF (granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor)
GM-CSF is a hematopoietic growth factor that stimulates the formation of colonies of neutrophils and macrophages in vitro and has the function of promoting the proliferation and development of early red megakaryocytes and eosinophilic progenitor cells.
GM-CSF is one of the first cytokines identified to have an effect on DC. The function of GM-CSF in DC culture is to promote the differentiation of monocytes into large macrophage-like cells, and the expression of MHC class II molecules on the cell surface is enhanced, thereby enhancing the antigen presentation function of cells. In addition, GM-CSF can also promote the survival of DC.
1.2 IL-4 (Interleukin-4)
The role of IL-4 in the induction of DCs by monocytes is to inhibit the overgrowth of macrophages, thereby directing monocytes to differentiate into DCs. If IL-4 is not added to the culture system, monocytes will differentiate into macrophages. At the same time, IL-4 also has the ability to reduce the expression of CD14 molecules on the cell surface. A decrease in the expression level of CD14 is an important marker for the differentiation of monocytes into DCs.
The interaction of GM-CSF and IL-4 can differentiate mononuclear cells into immature DCs. At this time, DCs have strong antigen uptake and processing ability, but antigen presentation ability is weak. MHC class I, class II molecules and B7 family molecules (CD80, CD86, etc.) are moderately expressed on the cell surface, but CD14 is not expressed.
1.3 TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α)
TNF-α can down-regulate the macrocytosis of immature DCs and the expression of surface Fc receptors, so that the intracellular MHC class II compartments disappear, but can up-regulate MHC class I and II molecules on the cell surface. The expression of B7 family molecules (CD80, CD86, etc.) differentiates immature DCs into mature DCs (mature DC). At this time, the antigen uptake and processing ability of DCs is significantly weakened, and antigen presentation ability is significantly enhanced, which is extremely active. T cells.
2. Cytokines and antibodies for CIK culture (ibid.)
[Cell preparation]
1. Collection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells
1.1 using a blood cell separator to collect 80-100 mL of the patient's own peripheral blood mononuclear cells;
1.2 Lymphocyte separation liquid density gradient centrifugation further purification of mononuclear cells (PBMC);
1.3 The serum-free medium was washed twice to obtain PBMC with a purity of more than 90%, and the number of cells should be 1-3×108.
2. (Optional step) Preparation of tumor antigen The tumor antigen for DC loading may be Tumor-Specific Antigens (TSA) or Tumor-Associated Antigens (TAA), or may be tumor whole cells. antigen.
DCs loaded with TSA or TAA have good targeting, but the method has the defects that the tumor-specific antigen or antigen peptide type is determined to be small and the immune attack of a single antigen often fails to kill tumor cells. The use of DCs loaded with tumor whole cell antigens overcomes these deficiencies because it is not necessary to know that those antigens are TSAs or TAAs of tumor cells, and that multiple tumor antigens in whole antigens can trigger DCs to produce cells against different antigenic determinants. Toxic T lymphocytes (CTL) are cloned to achieve effective killing of tumor cells.
There are many methods for tumor cell whole antigen-loaded DC, including loading DC with tumor cell lysate, DC with apoptotic tumor cells, DC with necrotic or dead tumor cells, DC with tumor living cells, and DC with tumor cells. Fusion and so on. At present, it is commonly used in clinical practice to load DC with tumor cell lysate, because the method is simple, rapid and effective.
Repeated freezing and thawing is a common method to obtain tumor cell lysate. The specific steps are as follows:
2.1 surgically resected tumor specimens, under sterile conditions, remove necrotic tissue and non-tumor tissue adjacent to the tumor;
2.2 Washing with sterile saline 3 times;
2.3 The tumor tissue was cut with a sterile tissue scissors, added to RPMI 1640 medium, and fully ground;
2.4 200 mesh sterile mesh filtration after collection of single cell suspension;
2.5 Resuspend the cells in RPMI 1640 medium to 1-2 x 107/ml and place in a 5 ml sterile cryotube;
2.6 The frozen tube was immersed in liquid nitrogen for quick freezing, taken out after 10 min, and then quickly thawed in a 37oC water bath for 10 min.
Repeat 3-5 times;
Note: It can also be freeze-thawed 3-5 times at -80 °C / 37 °C.
2.7 the tumor lysate was added to a centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min;
2.8 Collect the supernatant, filter and sterilize by 0.22μm filter, and check the protein content and bacteria, fungi and mycoplasma;
2.9 -80oC save spare.
3. CIK cell culture and identification
3.1 The PBMC obtained in step 1 was adjusted to a cell concentration of 2 x 106/ml with serum-free medium and placed in a culture flask;
3.2 Incubate for 2 h at 37 ° C in a 5% CO 2 incubator to allow monocytes to adhere;
3.3 collecting suspended cells, adjusting the cell concentration to 1-2 x 106/ml with serum-free medium;
3.4 adding 1,000 U/ml recombinant human IFN-γ culture;
3.5 After 24 h, 50 ng/ml CD3 monoclonal antibody and 300 U/ml recombinant human IL-2 were added to stimulate the growth and proliferation of CIK cells;
Note: 100 U/ml recombinant human IL-1 can also be added at this time.
3.6 Change the liquid or expand the bottle once every 3 days and add the recombinant human IL-2 300 U/ml;
3.7 On the 7th day of culture, CIK cells were harvested, and the number should be more than 1x109.
3.8 CIK Cell Quality Control:
3.8.1 Trypan blue staining to detect cell viability: live cells should be above 80%;
3.8.2 The expression of CD3, CD8 and CD56 on the cell surface was detected by flow cytometry, and the proportion of CD3+CD56+ cells was significantly increased.
4. Culture and identification of DC cells
4.1 The remaining adherent cells (mainly CD14+ monocytes) in step 3.2 were added to serum-free medium containing recombinant human GM-CSF 500-1,000 U/ml and recombinant human IL-4 500 U/ml at 37 °C. Cultured in a 5% CO2 incubator to induce differentiation of monocytes into DC cells;
4.2 Change the liquid once every 3d and fill the cytokines;
4.3 (optional step) On the 5th day of the culture, the tumor antigen 50 μg/ml obtained in the step 2 was added, and the antigen was loaded on the DC;
Note: This step is omitted if the antigen load is not applied to the DC.
4.4 On the 6th day of culture, recombinant human TNF-γ (500 U/ml) was added to induce DC cell maturation;
4.5 On the 7th or 8th day of culture, the number of DC cells should be harvested, and the number should be more than 1×106;
4.6 DC quality inspection:
4.6.1 Trypan blue staining to detect cell viability: live cells should be above 80%;
4.6.2 Flow cytometry detects the expression of HLA-DR, CD83 and CD86 molecules on the surface of DC cells to determine whether DC is mature.
5. Preparation and quality inspection of DC-CIK cells
5.1 The DC cells and CIK cells obtained in steps 4 and 3 were collected and co-cultured at a ratio of 1:10 (number ratio), and recombinant human IL-2 (300 U/ml) was added to the serum-free medium;
5.2 Change the liquid once every 3 days and add recombinant human IL-2 (300U/ml);
5.3 Collect cells on the 7th day, the number of cells should reach 1 × 1010 or more;
5.4 Quality inspection of DC-CIK cells:
5.4.1 Trypan blue staining test: live cells should be above 80%;
5.4.2 Flow cytometry to detect the expression of CD3, CD8, CD56 and other molecules on the cell surface: the proportion of CD3+CD56+ cells should be above 20%.
5.4.3 Cell killing experiment: DC-CIK cells are used as effector cells, and tumor cells (which may be primary tumor cells or tumor cell lines) are used as target cells, and effector cells and target cells are 10:1 (number ratio). The ratio was added to a 96-well U-shaped plate, and each well contained 1×104 target cells, and the final volume was 200 μl, and three replicate wells were set. After incubation for 4 h, the culture supernatant was taken, and the killing rate of the effector cells against the target cells was detected by a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) kit.
5.4.4 Before harvesting cells, take a small amount of culture for bacterial and fungal culture, and test for mycoplasma, chlamydia, and endotoxin (standard: negative for pathogen detection, endotoxin <5 Eu).
[step diagram] 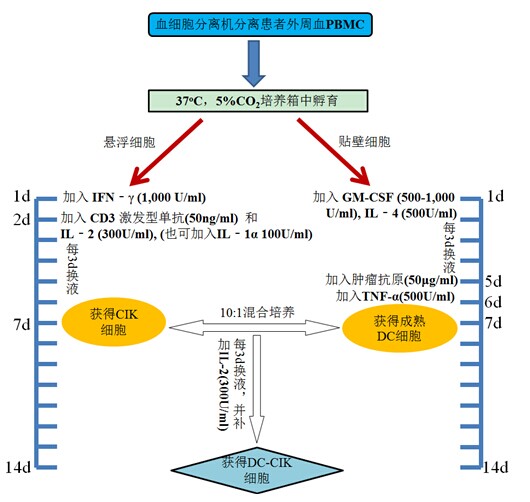
[Recommended reagent]
Manufacturer Product Name Product No. Product Specifications Use Concentration
eBioscience Anti-Human CD3 Functional Grade Purified 16-0037-85 500μg
PeproTech- biogems Anti-Human CD3 SAFIRE Purified 05121-25 100μg/500μg
PeproTech Recombinant Human GM-CSF (Animal Free) AF-300-03 20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50-100ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IFN-γ (Animal Free) AF-300-02 100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-1α (Animal Free) AF-200-01A 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 0.1ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-2 (Animal Free) AF-200-02 50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 30ng/ml
PeproTech Recombinant Human IL-4 (Animal Free) AF-200-04 20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 100ng/ml
Note: Animal Free means no animal content. The animal-free recombinant cytokine does not have any animal-derived substances in the production process, especially the incorporation of bovine protein, so that the recombinant human protein finally obtained does not contain any animal components. This can avoid contamination of animal pathogens (such as mad cow disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, etc.) and xenogeneic rejection and allergic reactions caused by foreign proteins. Therefore, it is preferable to use animal-free recombinant cytokines in cell culture in vitro.
[Other related reagents]
Manufacturer Product Name Product No. Product Specifications
PeproTech Recombinant Flt-3 Ligand (Animal Free) AF-300-19 10μg/50μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human IL-7 (Animal Free) AF-200-07 10μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human IL-15 (Animal Free) AF-200-15 10μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech Recombinant Human SCF (Animal Free) AF-300-07 10μg /50μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
[1] Steinman RM, Cohn ZA. "Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution". J. Exp. Med. 1973; 137 (5): 1142–62.
[2] Zhang Zhiwei, Song Xin. Standardization study of clinical preparation of DC-CIK cells. Chinese Journal of Oncology, 2011; 20(2): 85-88.
[3] Li R, Wang C, et al. Autologous cytokine-induced killer cell immunotherapy in lung cancer: a phase II clinical study. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012; 61:2125–2133. 
First, efficient CIK
High-efficiency cytokine-induced killer (CIK), a highly potent cytokine-induced killer cell, is one of the cellular immunotherapy methods for treating tumors and chronic infectious virus infections. The technique is to separate mononuclear cells from the patient's autologous peripheral blood (20-100 ml), and stimulate the expansion culture in vitro to obtain a subpopulation of cells which kills the killing effect of tumor cells and virus-infected cells under physiological conditions, mainly CD8+ killer T lymphocytes (CTL, approximately 70%) and natural killer cells (NK, approximately 10%) are extensively expanded and activated, and then returned to the patient one or more times. Efficient CIK as a adoptive immunotherapy for cells can effectively assist in the treatment of malignant tumors and chronic infectious virus infections.
1. High-efficiency CIK treatment indications (1) diagnosed as malignant tumor or EBV, CMV, HPV, HBV, HCV virus infection;
(2) Patients with an expected survival period > 3 months;
(3) Laboratory tests must meet the following conditions: absolute value of lymphocytes > 0.8 × 109 / L;
(4) The patient has the ability to know and can sign an informed or voluntary consent form;
(5) The patient has good compliance and can cooperate with the treatment of toxic and side effects;
(6) Anti-HIV(-), TPHA(-);
2. High-efficiency CIK treatment contraindications (1) combined with intracranial hypertension or unconscious brain tumors;
(2) Symptomatic heart failure or severe arrhythmia;
(3) Diffuse vascular internal coagulation;
(4) serum creatinine and / or urea nitrogen ≥ 1.5 times the normal value;
(5) sepsis or other uncontrollable infections;
(6) intestinal obstruction;
(7) After treatment, the heart condition is still unstable, and myocardial infarction occurred within 1 month before enrollment;
(8) Symptomatic peripheral neuropathy > Level 2 (NCIC-CTG standard);
(9) Uncontrollable diabetes;
(10) Severe mental disorders;
(11) Hypercalcemia, which is difficult to control with bisphosphonate, blood calcium concentration >12mg/100ml;
(12) Pregnant and lactating women;
(13) Concomitant infectious diseases: AIDS, syphilis, etc.;
(14) T lymphocyte-associated lymphoma and leukemia patients;
(15) Patients with severe T lymphocyte-associated autoimmune diseases;
(16) fever patients caused by infection;
3. Efficient CIK treatment plan (1) Individual use of the appropriate population Expected effect Use the program after surgery without other treatment of patients to prevent recurrence and metastasis • The first stage of return once a week, a total of 4-6 times return;
• The second phase returns every 2 weeks, a total of 4-6 times return;
• After that, it can be transferred once a week × 4 times every 3 months to half a year;
All other patients with ineffective tumor progression continued to improve quality of life and stable tumors • 1 time of reinfusion once a week, a total of 6-8 times after the return to evaluate the efficacy;
• Sustained every 1-2 weeks according to the progress of the patient, as required by the patient;
Chemotherapy or radiotherapy is effective but has been discontinued. Patients who need to maintain therapeutic effects maintain tumor stability for a long time. • Patients have no tumors.
o There are no other treatment options for patients after surgery;
• There are still tumors in the patient
o The first stage returns once a week, a total of 4-6 times return;
o The second phase returns every 2 weeks, a total of 4 times to return;
o According to the patient's request, it can be returned once every 2 weeks for a long time;
o Chemotherapy was administered 48 hours after the end of intravenous administration and returned on the 9th day;
o Calculate chemotherapy from the first day, return on the 7th and 14th day;
• Four weeks of chemotherapy
o On the 7th and 17th day of chemotherapy, each time you return 1 time;
• 8-day chemotherapy, three-week program
o Chemotransmission on the 3rd and 10th day;
o cell reinfusion is usually 48 hours after each targeted drug administration;
o High-efficiency CIK treatment plan after the end of targeted therapy refers to the separate use plan;
(2) The two persons check the patient's bed number, name, hospital number, blood collection time, blood collection amount, etc.;
(3) Tell the patient the purpose and method of blood collection, let the patient relax his emotions and avoid tension;
(4) Assisting the patient to take a supine position or a sitting position when collecting blood, exposing the vein, selecting thick, straight, and large veins, and collecting blood specimens under strict aseptic operation;
(5) Pay attention to observe the patient's complexion and mind during the blood collection process, and ask the patient if there is any discomfort such as dizziness or palpitation. If the patient has dizziness, fatigue, palpitations, etc., stop the blood collection, report the doctor, assist with the treatment, and complete the blood puncture point for 10 minutes. ;
(6) Shake the blood sample tube 180° upside down and shake it 5~8 times to achieve better anticoagulant effect. Then put the blood sample in the sealed bag, stick the seal and store it in the blood sample box (temperature 4~8) °C) immediately sent to the cell laboratory for cultivation;
(7) Fill in the cell culture blood sample collection nursing record sheet.
5. Precautions for the collection of high-efficiency CIK blood samples (1) Before blood collection, patients can drink warm water, low-fat and light diet;
(2) No infusion treatment can be performed before blood collection;
(3) One day before blood collection, patients may not be able to perform treatment and examination items that may damage or destroy lymphocytes, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, nuclear medicine examination, etc.;
(4) In the course of two consecutive courses of treatment, the blood and the transfused cells will cross in time, and the blood must be taken before the cells are returned;
(5) Blood routine within 3 days, requiring white blood cells in the normal range, and the absolute value of lymphocytes is greater than 0.8×109/L;
(6) The amount of blood collected depends on the absolute number of lymphocytes in the patient, and the blood collection amount is ×× lymphocyte count>0.8×109/L, which is about 20-100 ml;
(7) If the cells need to be frozen, the amount of blood collected needs to be increased;
(8) After the blood sample is collected, the aseptic operation box placed at 4~8 °C will be sent to the laboratory in time by the special person. The general specimen placement time cannot exceed 4 hours.
6. Efficient CIK reincarnation care (1) Psychological care, such as objectively explaining the efficacy and possible side effects of CIK, eliminating the doubts and fears of patients and their families, and achieving cooperation. Cell therapy as a new therapy brings hope to cancer patients, but there are individual differences in the efficacy, so that patients and their families should be fully informed, and patients can avoid psychological gaps due to failure to achieve the expected results;
(2) Determining the time of returning, informing the patient, and reasonably arranging the returning work according to the needs of the treatment;
(3) The CIK cells are sent to the ward, and the nurse should check the patient's name, hospital number, CIK number, preparation date, date of return, complete packaging, and cell quality test results with the laboratory staff;
(4) returning to the patient through the peripheral vein, strictly aseptic operation, pay attention to adjust the drip rate, first slow and fast; at the same time pay close attention to the general condition of the patient, such as body temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, etc., before and after infusion of cells Flushing with saline;
(5) During the infusion process, close inspection, gently squeeze the bottom of the transport bag 5-10 min to resuspend the precipitated cells to avoid cell sedimentation;
(6) Observation and nursing of side effects
1) fever, the most common side effect of CIK is fever, often occurs within 1-2 hours after reinfusion, and some patients have an exothermic reaction after 4 hours of reinfusion. A fever reaction occurs first to the doctor. In general, low or moderate fever can be treated without special treatment. Patients with phlegm drink more water. When high fever, follow the physical cooling of the doctor or ice or oral antipyretic drugs; observe the changes of the patient during the chill, keep warm, and give it when necessary. oxygen;
2) Allergic reactions, patients with rash, dyspnea, palpitations and other reactions, such as rare reactions in clinical, if the allergic reaction immediately stop the infusion, notify the doctor, give oxygen, anti-allergy treatment;
(7) After the return is completed, the outpatients are routinely observed for 30 minutes. If there is any discomfort, the nurses should be informed in time; if the patients have changed their condition after leaving the hospital, they should return to the clinic in time;
(8) Observe and record the patient's condition and fill in the cell return care record sheet.
7. Efficient CIK returning precautions (1) Before infusion of cells, they must be checked by two people before they can be entered;
(2) Carefully check the cell quality and check the cell test report;
(3) Using a disposable blood vessel, it is forbidden to use an infusion tube with a precision filter; use a scalp needle of No. 7 or above to avoid damage to the cells caused by the shear force generated by the small needle;
(4) prohibiting the addition of other drugs to the cells;
(5) Pay attention to the infusion speed, the initial speed is 30~40 drops/min. If there is no special reaction after 10min observation, change the drip rate to 60~80 drops/min, and lose within 40~60 minutes;
(6) After the cell culture, it should be returned in time. If it needs to be stored, it must be stored in the refrigerator at 2~8 °C for no more than 8 hours;
(7) Before and after radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the cells should be returned at a time interval of 48 hours to prevent CIK cells from being killed by radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which may affect the curative effect.
Second, DC-CIK
With the improvement of cell preparation technology, DC-CIK cell adoptive immunotherapy has been gradually developed in the clinic, and relevant reports are available. In experimental research, Marten experimental studies have shown that DC and CIK co-culture can simultaneously promote the proliferation and immune function of CIK cells and DC cells. Experimental studies by Zhang et al. showed that the application of DC-CIK cells after chemotherapy can effectively inhibit the growth of tumor cells and even completely disappear the tumor; and the anti-tumor effect of DC-CIK cells does not harm the function of the collective immune system. When tumor-specific antigens are relatively poorly understood, the application of DC-CIK cells as adjuvant therapy for tumor chemotherapy and postoperative surgery has important clinical significance.
Third, the principle of DC treatment for tumor treatment 1DC can express MHC class I and MHC class II molecules, MHC molecules bind to their captured tumor antigens, form peptide-MHC molecular complexes, and present them to T cells, thus The MHC class I restricted CTL reaction and the MHC class II restricted CD4+ Thl reaction were initiated. At the same time, DC also initiates an immune response by providing a second signal necessary for T cell activation through its highly expressed costimulatory molecules (CD80/B7-1, CD86/B7-2, CD40, etc.).
Binding of 2DC to T cells can secrete IL-12 and IL-18 to activate T cell proliferation, induce CTL production, lead Th1 type immune response, and facilitate tumor clearance; activate perforin P granzyme B and FasL/Fas mediated pathway enhancement NK cytotoxicity;
3DC Chemotactic Cytokines (CCK) specifically chemotactic primary T cells promote T cell aggregation and enhance T cell activation. Preservation of effector T cells persists in the tumor site, possibly affecting the formation of tumor blood vessels by releasing certain anti-angiogenic substances (such as IL-12, IFN-γ) and pro-angiogenic factors. The above CCK further activates DC by positive feedback paracrine, up-regulates the expression of IL-12, CD80 and CD86; meanwhile, DC also directly presents antigenic peptide to CD8+ T cells, and activates CD8+ T cells with the help of activated CD4+ T cells. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells can further enhance the body's anti-tumor immune response by secreting cytokines or directly killing.
Fourth, ACTL
The full name is "AAV-DC-CTL targeted anti-tumor cell immune technology", referred to as "ACTLTM" or "ACTL technology" or "ACTL tumor cell targeted therapy".
"ACTLTM Anti-Cancer Cellular Immunotherapy"
On October 3, 2011, Professor Steinman, a Canadian scientist, American Medical Association, and a member of the National Academy of Sciences, won the 2011 Nobel Prize in Medicine. Steinman's award was due to his discovery of "Dendritic Cell (DC cells) and its role in the adaptive immune system." At the beginning of the 21st century, Professor Liu Yong from the Cancer Center of Stanford University School of Medicine, under the guidance of Professor Steinman, combined his research with recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) and DC cells studied by Professor Steinman. Development of transfected DC cells with recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying one or several specific tumor-associated antigenic determinant genes, stimulates T lymphocytes in vitro, and produces cells that specifically kill one or several tumor-associated antigen-positive tumor cells Cytotoxic Lymphocytes (CTL cells), followed by relevant clinical trials, were successful. This treatment technology is called ACTL tumor cell targeted therapy technology and has obtained 5 international patent protections. The cytotoxic T lymphocytes specifically prepared by this technology to kill tumor-associated antigen-positive tumor cells are called specific killer T cells (ACTL). , A stands for specific antigen) has high potency, targeting (ie specificity) to kill one or several specific tumor-associated antigen-positive tumor cells and PSMA-positive tumor neovascular endothelial cells, and has no damage to normal cells. effect.
A typical example of clinical application of ACTL tumor cell targeted therapy technology is Professor Steinman's treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer and the treatment of Apple's advanced Steve's cancer. Professor Steinman has only used this treatment technique and has a survival time of 4 years.
After several years of clinical research at Stanford University Cancer Center, it was proved in 2010 that ACTL-specific killer T cells can not only directly target tumor cells, but also block tumor neovascularization, play an indirect role in killing tumor cells, and significantly improve clinical performance. Efficacy. The results of this research were named the most important breakthrough in the field of cancer biotherapy in the first half of 2010 by the 2010 American Society of Oncology (ASCO).
Clinical studies conducted in the United States have shown that ACTL-specific killer T cells may not only reverse the resistance of gynecological and prostate malignant tumors to anti-hormone therapy, but also may reverse tumor cells to Yi_瑞_沙,阿_瓦_ Drug resistance of molecular targeted drugs such as Si-Ding.
AAV-DC-CTLTM tumor cell targeted therapy technology is to transform the pathogenic wild-type adeno-associated virus (AAV) into a recombinant adeno-associated antigen carrying a specific tumor-associated antigenic determinant gene by genetic recombination technology. The virus, which infects peripheral blood mononuclear cells (Monocytes. Mo), is induced by cytokines, and the monocytes are transformed into DC cells with powerful antigen-presenting functions. The DC cells obtained by this technique stimulate T lymphocytes of patients in vitro to produce Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) which effectively kill tumor cells. The produced CTL has tumor antigen specificity, ie, targeting, and has a killing effect only on one or several specific tumor-associated antigen-positive tumor cells and PSMA-positive tumor neovascular endothelial cells, and has no antigen-negative cells. effect.
CTL cells are a subset of T cells of CD8+, which is a specific T cell, which has direct killing effect on certain viruses and tumor cells, and constitutes an important anti-virus and anti-tumor line of defense against natural killer cells. The CTL killing mechanism is:
Recommended products and related product summary tables:
First, CIK
Manufacturer Product Name Product No. Product Specifications Use Concentration Recommended Products
eBioscience Anti-Human CD3 Functional Grade Purified 16-0037-85 500μg
PeproTech- biogems Anti-Human CD3 SAFIRE Purified 05121-25 100μg/500μg
PeproTech recombinant human IFN-γ (AF) AF-300-02 100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-1α (AF) AF-200-01A 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 0.1ng/ml
PeproTech recombinant human IL-2 (AF) AF-200-02 50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 30ng/ml
Related Products
PeproTech é‡ç»„人Flt-3 Ligand (AF) AF-300-19 10μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-7 (AF) AF-200-07 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-15 (AF) AF-200-15 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人SCF (AF) AF-300-07 10μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg
①释放穿å”ç´ ï¼Œé¢—ç²’é…¶ï¼Œè£‚è§£é¶ç»†èƒžã€‚
②通过FasL介导é¶ç»†èƒžçš„凋亡。
二〠DC-CIK
生产商 产å“å称 产å“ç¼–å· äº§å“è§„æ ¼ 使用浓度推è产å“
eBioscience Anti-Human CD3 Functional Grade Purified 16-0037-85 500μg
PeproTech- biogems Anti-Human CD3 SAFIRE Purified 05121-25 100μg/500μg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人GM-CSF (AF) AF-300-03 20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50-100ng/ml
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IFN-γ(AF) AF-300-02 100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 50ng/ml
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-1α(AF) AF-200-01A 10μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 0.1ng/ml
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-2 (AF) AF-200-02 50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 30ng/ml
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-4 (AF) AF-200-04 20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 100ng/ml
Related Products
PeproTech é‡ç»„人Flt-3 Ligand (AF) AF-300-19 10μg/50μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-7 (AF) AF-200-07 10μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人IL-15 (AF) AF-200-15 10μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
PeproTech é‡ç»„人SCF (AF) AF-300-07 10μg /50μg /100μg /250μg /500μg /1mg
阅读原文:http://