Fruit Single Packed Sweet Corn
What are the benefits of eating a vegetarian diet on a regular basis?
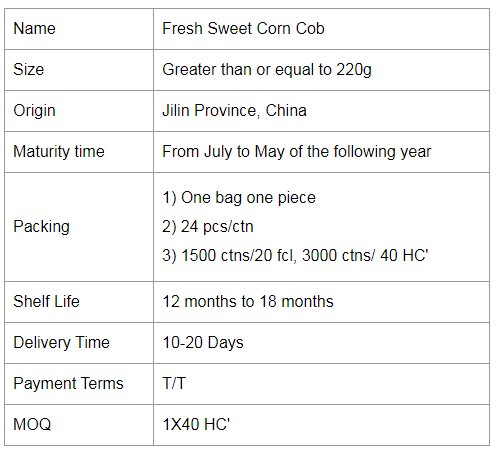
If you have any questions, please contact us directly. If you have any questions, please email us directly. Sweet Corn Fresh,Delectable Sweet Corn,Sweet Corn Healthy,Baked Sweet Corn Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com
1. People who eat vegetarian food regularly will live longer than those who eat meat regularly, as Indian tribesmen live longer because of their regular vegetarian diet and many monks live longer because of their regular vegetarian diet. The fat content of sweet corn is 2 grams of fat per 100 grams, making it a low-fat product.
A single cob pack of sweet corn from Jilin Province Agricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. is at least 220g and will provide you with at least 6.38g of protein and 4.4g of fat.
2. Corn as a vegetarian food is lower in calories than other foods of the same quality, and its fat content is almost non-existent. It provides the body with the nutrients and vitamins it needs and has no energy stores.
3. Reduces cholesterol levels. Vegetarians have less cholesterol in their blood than meat eaters. If cholesterol levels in the blood are too high, it often causes blood vessels to become clogged.
4. It reduces the burden on the kidneys. Once meat eaters eat meat containing animal blood, the burden on the kidneys is even heavier".


Breeding Management Technology of Female Breeds
First, empty breeding female rabbit breeding management empty bear period refers to a period of time when the pups are weaned until they become pregnant again. (1) Physiological characteristics of empty female rabbits: Empty female rabbits consume a lot of nutrients during breast-feeding, and the body is relatively thin. Therefore, various nutrients are needed to compensate to improve their health level. The leisure period is generally 10 to 15 days. If there is no relaxation period if the frequency of breeding is used, the pups will be bred before weaning and will enter the gestation period after weaning. (2) Breeding of empty female rabbits: The nutrition of breeding empty female rabbits must be comprehensive. In the abundant season of green grass, as long as there are sufficient high-quality green feeds and a small amount of fine materials, the nutritional needs can be met. In the old season of green feed, it is necessary to supplement the juicy feed such as carrots, and it is also possible to supplement the feed properly. Empty female rabbits should maintain a proper fatness of 70% to 80% of their weight. Over-fat or too-lean female rabbits can affect estrus and breeding. The ratio of protein and carbohydrate content in the diet should be adjusted. Too thin female rabbits should be refined. The amount of material fed to quickly restore body fat; overweight female rabbits to reduce the amount of fine feed, increase exercise. (3) Management of empty female rabbits: The management of air-breathing female rabbits should be done in the air circulation in rabbit houses, rabbit cages and rabbit bodies should be kept clean and sanitary, and rabbits that have not been exposed to light for a long time must be replaced by well-lit cages. In order to promote the body's metabolism, the normal activities of the female rabbit's sexual function are maintained. For the long-term non-estrus female rabbits, heterosexual induction or artificial aphrodisiacs can be used. Second, the feeding and management of pregnant female rabbits Pregnant female refers to the period of mating from pregnancy to delivery. The nutrients needed by the female rabbit during pregnancy, in addition to maintaining its own needs, also meet the needs of the embryo, breast development and uterine growth. Therefore, it takes a lot of nutrients. According to measurements, females weighing 3 kg, the total weight of the fetus and placenta up to 650 grams. Among them, dry matter was 16.5%, protein was 10.5%, fat was 4.5%, and inorganic salt was 2%. At 21 days of gestation, the protein content of the fetus was 8.5%, 10.2% at 27 days, and 12.6% at first birth. At the same time, the metabolic rate in pregnant females also increases with embryonic development. (1) Feeding pregnant female rabbits: Feeding pregnant female rabbits is mainly to supply female rabbits with full-priced nutrients. According to the growth and development of the fetus, different feeding levels can be adopted. However, if the pregnant female rabbit has too much nutrient supply, over-obesity of the female rabbit may also have an adverse effect, which is mainly manifested by the decrease in the number of fetuses and postpartum lactation. According to experiments, the number of implantations of fertilized eggs was observed on the ninth day after mating. As a result, the embryonic mortality rate of German long-haired rabbits fed with high nutrient levels was 44%, while that of normal long-haired rabbits fed only 18%. Therefore, in general, pregnant female rabbits should be controlled at 150-180 g per day when they feed pelleted feeds freely; in the case of free-feeding basic feeds (green and coarse) and supplemented with mixed concentrates, daily Plus mixed concentrate should be controlled at 100 to 120 grams. The nutrients needed for pregnant female rabbits are most important with proteins, inorganic salts and vitamins. Proteins are important nutrients that make up the fetus, and calcium and phosphorus in inorganic salts are essential for fetal bone growth. If the amount of protein in the feed is insufficient, it will cause an increase in stillbirth, a decrease in the birth weight of the pups, and a decrease in viability. The lack of inorganic salts will make the puppies lean and easy to die. Therefore, maintaining the appropriate nutrition level during the pregnancy period, especially during the late pregnancy, of female rabbits plays an important role in improving maternal health, increasing milk yield, and promoting the growth and development of fetuses and pups. (2) Management of pregnant female rabbits: The management of pregnant female rabbits is mainly to do good care and prevent miscarriage. Female abortion usually occurs within 15 to 25 days after pregnancy. Causes of abortion can be divided into mechanical, nutritional and disease. Mechanical abortions are mostly caused by catching, scaring, improperly touching the tires, and squeezing. The majority of nutritional abortions are due to inadequate nutrition. Suddenly changing the feed, or due to moldy degeneration, frozen feed, etc. There are many diseases causing miscarriage, such as pasterellosis, salmonellosis, Treponema and genital diseases. In order to prevent abortion, the female rabbit should be 1 cage after pregnancy to prevent extrusion; do not catch it for no reason, touch the tire when the action should be light; feed should be clean and fresh; find the sick female rabbit should identify the reasons for timely treatment . Management of pregnant female rabbits also needs to do prenatal preparations. Normally, the litter box should be prepared 3 to 4 days before the childbirth. After cleaning and disinfecting, the bottom of the box should be covered with a layer of dried straw and soft straw. The litter box should be placed in the cage 1 to 2 days before the childbirth to provide nesting for the female rabbits. The delivery room should be staffed with special personnel, winter indoor cold insulation, summer summer mosquitoes. Third, the nursing mother rabbits feeding and management Female rabbits from the time of childbirth to weaning piglets during this period known as lactation. The period during which the female rabbit is breast-feeding is the heaviest burden, and the quality of feeding and management has a great influence on the health of the female rabbit and the young rabbit. During lactation, the female rabbit can secrete 60 to 150 milliliters of milk per day, and high-yield female rabbits can reach 200 to 300 milliliters. In addition to the lower lactose content of rabbit milk, the protein and fat content is more than 3 times higher than that of cow and goat milk, and the inorganic salt is about 2 times higher. It was determined that the amount of postpartum lactation was gradually increased in the female rabbit, reached the peak of lactation at about 3 weeks postpartum, and then the amount of lactation decreased gradually. (1) Feeding of lactating female rabbits: Nursing female rabbits consume a large amount of nutrients every day in order to maintain life activities and produce milk, and these nutrients must be obtained from the feed. Therefore, feeding and nursing female rabbits must be fed easily digestible and nutritious feeds to ensure adequate supply of protein, inorganic salts and vitamins. If the fed feed does not meet the nutritional needs of the nursing mother rabbit, a large amount of nutrients stored in the body will be used, thereby reducing the weight of the female rabbit, damaging the health of the female rabbit and affecting the milk production of the female rabbit. Feeds fed to lactating female rabbits must be clean and fresh. At the same time, some concentrated feeds and inorganic salt feeds, such as bean cakes, bran, bean dregs, and salt, bone meal, etc., should be properly added to ensure sufficient drinking water every day to meet the nursing mothers. Rabbits require moisture. The quality of feeding and nursing female rabbits can generally be identified based on the feces of the pups. If the litter box is kept clean and dry, there is very little urinary excretion in rabbits, and the pups eat very well, indicating that they are feeding well and are nursing normally. If there is too much urine, it means that the water content in the female rabbit's feed is too high; if the stool is too dry, it means that the female rabbit has insufficient drinking water. Feeding moldy feed can also cause diarrhea and indigestion. Some rabbit farms use mother rabbits and puppies separately to feed them. The method of regular breastfeeding is to remove the pups from the female rabbit cages and place them in appropriate places. When they are breast-feeding, puppies are sent back to the female rabbit cage. In the early stages of delivery, breastfeeding can be performed twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, and once a day after 20 days, it can be fed once a day. The advantages of this feeding method are: to understand the lactation situation of female rabbits, to reduce the freezing and thawing of young rabbits, to control the estrus of female rabbits, and to achieve timely breeding; to prevent the mother from rushing to eat, and to enhance the constitution of female rabbits; and to reduce the infection of coccidiosis. Opportunity; Fostering independent living ability of pups. (2) Management of lactating female rabbits: The management of lactating female rabbits is mainly to keep the rabbit houses and rabbit cages clean and dry. Rabbit cages should be cleaned every day, and the feeding utensils and urine feces should be washed, and disinfection should be performed regularly. In addition, we must constantly check the female rabbit's nipples, breasts, to understand the lactating situation of the female rabbits, such as the discovery of a lump in the breast, nipple swelling, broken, and timely treatment.