Research using equipment The newly published research results reveal that the signal function of Arabidopsis NRT1.1 regulates ammonium absorption and CN metabolism uncoupling, and enhances the sensitivity of plants to ammonium stress. The research results provide theoretical support for understanding the mechanism of plant ammonium toxicity and improving the nitrogen nutrient use efficiency of rapeseed under rice field waterlogging conditions. It was found that in the (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 environment, NRT1.1 enhances the absorption of NH 4 + in the growing environment by signaling regulation of the expression of NH 4 + absorption transporter in the root; in addition, the root NH 4 + The assimilation pathway GS/GOGAT cycle was significantly reduced, while the PK enzyme activity was not significantly affected, resulting in a large accumulation of NH 4 + in plants, imbalance of carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and induction of ethylene production, promoting plant senescence. The NH 4 + uptake transporter in the nrt1.1 mutant root was not significantly induced by (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , and the GS/GOGAT cycle was not significantly affected, while the activity of GDH was significantly increased by absorption and assimilation of NH4+. The synergy between the plants reduces the accumulation of NH4+ in the plants and alleviates the occurrence of ammonium toxicity. In this study, the NMT biophysiology detector Physiolyzer ® was used to detect the rate of NH4+ efflux in the root zone of rapeseed. The rate of NH4+ in the root tip of the mutant was significantly higher than that in the wild type. Improve Immunity Plant Extract Improve Immunity Plant Extract,Ginseng Extract,Mulberry Powder,Seabuckthorn Powder Fufeng Sinuote Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.ffsinuoteplant.com
Plant Physiol : Application of NMT in the efficient utilization of nutrient in rice oil rotation 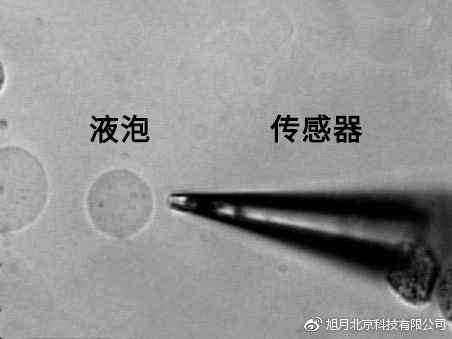
In the previous article, NMT was used to detect the transmembrane NO 3 - transport of rapeseed root vacuoles, and it was found that the rate of NO 3 - in low-nitrogen utilization (NUE) rapeseed was 3 times higher than that of high NUE canola. a high proportion of NO 3 - assigned to the cytoplasm, which in turn induce the expression of the root NRT1.5 while suppressing the expression of NRT1.8, resulting in a greater proportion of NO 3 - loaded into the xylem sap transported to the aerial parts of rapeseed. This is one of the important reasons for the higher NUE of nitrogen-efficient rapeseed genotypes under rice oil rotation. 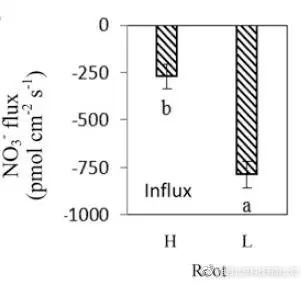
High (H), low (L) NUE rapeseed root vacuole NO 3 - transmembrane absorption rate 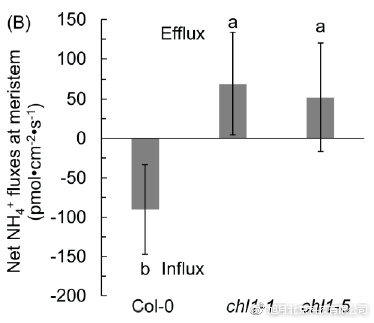
Comparison of NH4+ efflux rates in the apical and meristematic regions of the mutant.
Detection of transmembrane transport of vacuoles in rape roots by non-invasive micro-measurement
NMT Physiological Tester NMT Physiolyzer ®
October 2018, Hunan Agricultural University, Professor Zhang Zhenhua team for research waterlogging problems affecting the efficient use of nutrients in the rice fields of rapeseed, published in Plant Physiology, study titled "NRT1.1-related NH 4 + toxicity is associated with a disturbed balance Between NH 4 + uptake and assimilation". This is the second article published by Professor Zhang Zhenhua on the Plant Physiology using Non-invasive Micro-test Technology (NMT).