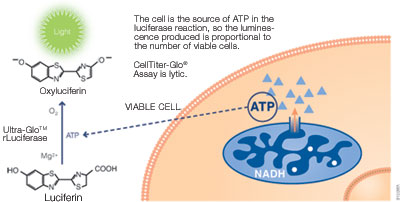
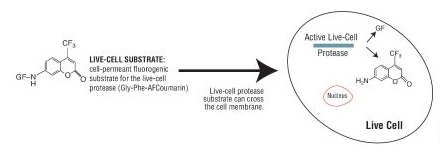
Cell viability is an important indicator for judging whether cells in vitro can grow normally under certain conditions, such as drug treatment, radioactive or ultraviolet irradiation, and changes in culture conditions. There are many methods for detecting cell activity, such as trypan blue staining, cloning (colony) formation, ATP content determination, fluorescent staining, and colorimetry (MTT). I. Determination of ATP Content---Bioluminescence Detection Studies have shown that the amount of endogenous adenosine triphosphate (ATP) can reflect the activity of cells. Endogenous ATP is the most basic energy source of living cells. When cells die, ATP is rapidly hydrolyzed. Therefore, measuring the content of endogenous ATP in cells can reflect the activity of cells and the number of viable cells in time. ATP-based cell viability assay is a sensitive and reliable assay. The reaction principle is that under the conditions of aerobic and ATP, the luciferase catalyzes the fluorescence of fluorescein (wavelength is 562 nm), and the intensity is positively correlated with the ATP content. Therefore, the measured fluorescence intensity can indirectly reflect the amount of viable cells. Promega CellTiter-Glo® Luminescent Cell Viability Assay is a rapid cell viability assay based on ATP detection. (Catalog No.: G7570) - Detection type: illuminate - Detection marker: ATP -Application: cell viability, cell proliferation, cytotoxicity - Cell type: cell line, primary cell (suspended or attached) - Detection step: one-step method, homogenization detection -Operation time: 10min - Sensitivity: 10 live cells (96-well plates) Second, the fluorescence detection Some fluorescent dyes have different effects on dead cells and living cells, and cell viability is detected by fluorescence microscopy. For example, propidium iodide (PI), which is repelled by living cells but penetrates the cell membrane of dead or dead cells, so living cells are not stained by dyes, and only dead cells or apoptotic cells can be stained red. Acridine orange (AO) penetrates the cell's DNA through the intact cells of the plasma membrane, giving it a bright green glow. Ethidium bromide (EB) can only penetrate the cells damaged by the membrane, embed DNA, and emit orange-red light. Cell viability can also be identified using AO-EB double staining. Compared with traditional dyes, this detection method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, easy operation, easy to distinguish, and can distinguish living cells, early apoptosis cells, late apoptotic cells and dead cells by double staining. It has a wide range of applications in the detection of apoptosis. Alamar Blue is a safe, stable, water-soluble, non-toxic, cell-inducing dye that indicates cell metabolism through fluorescence or color changes. Living cell mitochondrial enzymes are capable of converting the blue oxidized form, Alamar Blue, into a red, reduced form, with quantifiable fluorescence changes, and inactive cells cannot restore Alamar Blue. The intensity of fluorescence or the intensity of red reflects the degree of cell proliferation. The color change can be measured by a microplate reader; the fluorescence change can be detected by a fluorometer, the excitation wavelength is 530 nm, the scattering wavelength is 590 nm, and the fluorescence method has better sensitivity. The AlamarBlue method is easy to operate, specific and sensitive, and has good reproducibility. The use of AIamar Blue does not affect the normal metabolism and gene expression of the cells. It can be continuously cultured and expanded under the conditions of aseptic conditions, which is conducive to the continuous culture of cells. Monitoring and in-depth research. However, since the decomposition product of Alamar BIue is reddish, only phenol red-free medium can be used, and the time requirement for culture is also harsh compared to the MTT method. Promega CellTiter-FluorTM Cell Viability Assay is an innovative fluoro method that is a non-lytic live cell assay for detecting the viability and quantity of living cells. (Catalog No. G6080) Principle: This system detects protease activity in living cells, which is a conserved constitutive protein and thus serves as a biomarker for cell viability. The live cell protease activity is only associated with intact living cells and is detected by a fluorescent peptide substrate (Gly-Phe-AFC) that penetrates the cell membrane. After entering the living cells, the substrate is cleaved by a living cell protease to produce a fluorescent signal whose intensity is related to the number of viable cells. When the integrity of the cell membrane is lost and leaks out into the surrounding medium, the activity of the living cell protease disappears. - Detection marker: live cell protease - Detection type: Fluorescence (380-400 nm excitation light / 505 nm emission light) -Application: cell viability, cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, additive detection - Cell type: cell line, primary cell (suspended or attached) - Detection step: one-step method, homogenization detection -Operation time: 0.5-3h - Sensitivity: 40 live cells (96-well plates) Third, colorimetric detection MTT colorimetric assay was first initiated by Mosmann in 1983. The principle is that succinate dehydrogenase in mitochondria in living cells can be MTT [chemical name 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazole-2)- 2, 5-Diphenyltetrazolium bromide, the appearance of light yellow] reduced to blue-violet crystalline formazan, and deposited in cells, while dead cells do not have this function. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) dissolves the hyperthyroidism in the cells, and the color of the solution is proportional to the amount of formazan contained. The OD value was measured at a wavelength of 570 nm using a microplate reader. The MTT method can easily and quickly determine the cell proliferation response, and can avoid the test error caused by human manipulation factors, greatly improving the accuracy and reproducibility of the experimental results. Most of the MTT methods are currently used to detect growth and proliferation of cultured cells, screening of new drugs, cytotoxicity tests, and tumor cell sensitivity tests. In addition, its low price has become one of the preferred methods for measuring the cell viability of various laboratories. However, the MTT method is not suitable for suspending cells, because the culture solution needs to be aspirated before dissolving the formazan. This step is likely to cause the loss of formazan, which leads to deviation of the experimental results. If the medium is not removed, serum and phenol red in the medium will affect the results of the experiment. In order to eliminate the effects of serum and phenol red in the culture solution, an improved MTT method has been proposed. That is, under the premise of not taking out the medium, some organic solvents, such as acidified SDS, SDS-DMF acidic solution, etc., directly dissolve the formazan, and have achieved good results. For the shortcomings of MTT, which is insoluble in water, the researchers have developed a variety of water-soluble tetrazolium salts: XTT, CCK-8 (also known as WST-8). Both XTT and CCK-8 are newly synthesized tetrazole nitrogen derivatives, which are similar to MTT and can be degraded by dehydrogenase in mitochondria of living cells to produce brown-yellow water-soluble formazan, which can directly pass through the spectrum. The OD value was measured by absorption, and the proliferation of the cells was estimated. When used in combination with the electronic coupling agent PMS, it can also enhance its reduction reaction and improve the sensitivity of the reaction. Compared with the MTT method, the main advantage of these methods is that the reaction product is water-soluble, does not require the use of a lysate to dissolve the precipitate, and does not need to absorb the supernatant, and is suitable for adherent and suspension-grown cells, shortening the detection time and reducing the number of treatment steps. It also greatly improved the sensitivity of the experiment. The disadvantage is that the cost is high, the XTT aqueous solution is unstable, needs to be stored at a low temperature or is ready for use; and the color of the CCK-8 reagent is light red, which is close to the color of the medium containing phenol red, and the unattended activity is likely to cause leakage or More plus. The Promega CellTiter 96® AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay is a novel cell viability assay for colorimetric assays. One-step operation, get rid of the complex problems of traditional MTT operation, small error, no need to dissolve organic solvent, no need to remove supernatant, live cell detection, etc. (Catalog No. G3582  G3580  G3581 ) - Detection type: absorption light (490nm) - Detection marker: mitochondrial dehydrogenase -Application: cell viability, cell proliferation, cytotoxicity - Cell type: cell line, primary cell (suspended or attached) - Detection step: one-step method, homogenization detection -Operation time: 1-4h - Sensitivity: 1000 live cells (96-well plates) Double Door Safe Box,Home Safe Box,Ammunition Safe Box,Gun Safe Hebei Tiger Brand Group Jia Bao Cabinet Industry Co. LTD , https://www.cntigersafe.com